
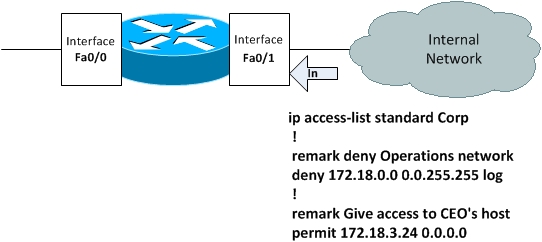
Destination Address Address Type VLAN Destination PortĠ000.856b.

If you were looking for a device you could ping it, look at the arp table to get the mac then use the mac command to find the port. It is used to record a stations mac address and it’s corresponding switch port location."Įxample: Port 17 has a device plugged in with this mac address. Here is a quote from "The CAM table, or content addressable memory table, is present in all Cisco Catalysts for layer 2 switching. I know you don't want to know about the ARP command but this command and the ARP command together you can find devices on your switches. From this user interface, you can directly execute all Cisco IOS commands, and it doesn’t matter how you reach the Cisco IOS platform you can enter any CLI command from a remote, console, or terminal interface. I'm not sure why it's labeled Destination Address. The Cisco IOS CLI is the main user interface for configuring, maintaining, and troubleshooting most Cisco devices. The MAC table or CAM table only records source addresses. To define the MAC Extended ACL, use the mac access-list extended command. It identifies the mac address that is on that port. access-list-nameName of a MAC ACL to apply to an interface or subinterface (as specified by the mac access-list extended command). The column title in the command is a destination address. Example: Router(config-if-srv) mac access-group macext2 in: To use a MAC access control list (ACL) to control inbound traffic on an Ethernet service instance. It will show multiple MAC addresses on the uplink port that connects to other switches. Thats why I showed it two different ways.

Some switches/ios versions have a slight variation of the command. It will show multiple MAC addresses on the uplink port that connects to other switches. Show mac-address table or show mac-address-table will give you the interface (the given name, not the name you assign it) and MAC Addresses.
That's why I showed it two different ways. Switch01(config-if)#mac-address mac-address table or show mac-address-table will give you the interface (the given name, not the name you assign it) and MAC Addresses. You need to key in 20 times of MACS each port!Įnter configuration commands, one per line. Imagine of you have 20 hosts and switch with 24-ports. Register all MACs in each individual port.įor smaller network, if you do not have authentcation/radius server, you probably can register mac addresses in the switchport, BUT this is a less-preferred solution.
You need to key-in all MACs.Įxtended MAC Access List configuration commands:Įxit Exit from MAC Named ACL configuration mode If you have VLAN, use ACL to filter MAC (without authentication server).
#Cisco mac address access list how to
You can refer to the following links on how to configure 802.1x for access devices:ġ. Enable aaa authentication your switch as well. 802.1x uses radius authentication protocol. This will prevent anyone, including visitors to easily gain access to your network.īut to achieve this, you need authentication server like Cisco ACS. User need to use their own user ID & password. With this, any machine connected to your faceplate/network (which is connected to switchport enabled with 802.1x) will get authentication prompt. But you can use feature called 802.1x (switch port authentication) Q: How can I provide access to network with know MAC address list? I have to prevent visitors plugging their laptop into our network.Ī: So far, MAC address suthentication is only available for wireless AP only.
Q: Is there any way to get the MAC address of all the end nodes from the switch?Ī: From the switch, issue command 'show arp' or 'show mac-address-table'. <1100-1199> Extended 48-bit MAC address access list <1300-1999> IP standard access list (expanded range) <200-299> Protocol type-code access list <2000-2699> IP extended access list (expanded range) <2700-2799> MPLS access list <300-399> DECnet access list <700-799> 48-bit MAC address access list.

 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
